OTHER SERVICES
Robotic Process Automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a software technology that makes it easy to build, deploy, and manage software robots that emulate humans’ actions interacting with digital systems and software. Just like people, software robots can do things like understand what’s on a screen, complete the right keystrokes, navigate systems, identify, and extract data, and perform a wide range of defined actions. But software robots can do it faster and more consistently than people, without the need to get up and stretch or take a coffee break.
What are the business benefits of RPA?
Robotic process automation streamlines workflows, which makes organizations more profitable, flexible, and responsive. It also increases employee satisfaction, engagement, and productivity by removing mundane tasks from their workdays.
RPA is non-invasive and can be rapidly implemented to accelerate digital transformation. And it’s ideal for automating workflows that involve legacy systems that lack APIs, virtual desktop infrastructures (VDIs), or database access.
When is a process suitable for automation?
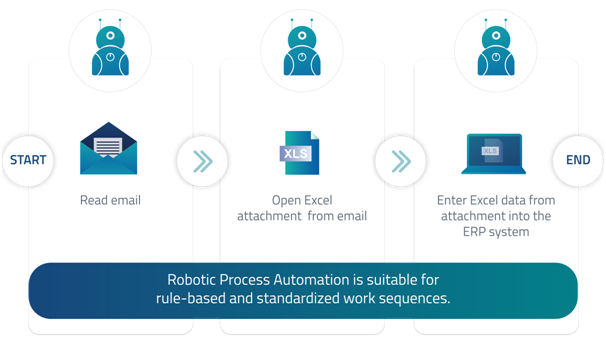
In order for a software robot to know which processes it should execute and how, structured data must be available in advance. Rule-based and standardized work sequences are suitable processes for automation by RPA. They always follow the same instructions for action and vary little or not at all. Activities with long runtimes that require time-consuming manual processing by users and are therefore particularly likely to result in errors offer enormous potential for Robotic Process Automation as well. A specific sequence provides the robot with the respective process sequences. These are often created in flowcharts and serve as specifications for the RPA system's activities. Since the software bot always follows the same decision rules, each process step must be specified in the flowchart.
If all the required information is available to the bot in a structured form, it can act on the basis of the previously defined workflow and execute the tasks automatically at high speed. When certain steps are missing or the data is incomplete, the digital robot will arrive at an incorrect result. Processes that change frequently or do not have clear decision criteria are therefore less suitable for automation. If there are changes to the specifications of already defined process flows, they can be adapted flexibly at any time.
Robotic Process Automation application areas:
Customer Service
- automated processing of customer inquiries
- easy customer data management
- quick document review
Accounting
- digital billing management
- easy changes to the master data in payroll accounting
- automated transaction reporting processes
Financial Services
- easy management of examination requests
- simple account maintenance
- automated processing of incoming and outgoing invoices
Human Resources
- structured on- and offboarding
- fast updating of employee data
- simple preparation of employment contracts
Sales & Marketing
- uncomplicated report creation
- fast quotation
- automatic newsletter sending